Table of Contents
Intorduction
The armarx::SimoxCSpace uses simox to check whether a defined scene with one agent is collision free for a given configuration. This class is used by planning algorithms (e.g.: RRTConnect) to do discrete collision checking and implicitly defines a configuration space (c-space).
The armarx::SimoxCSpace holds a set of stationary objects specifying the scene and one agent. The agent may have objects attached to it.
Create an cspace
You will need some proxies to memory segments:
armarx::SimoxCSpace uses the memoryx::CommonStorage to load collision models for objects. You will use the memoryx::PersistentObjectClassSegment to load objects (memoryx::ObjectClass). If you have another source for memoryx::ObjectClasses you can use it instead.
To create an empty cspace use:
Add objects
Each object in the scene is defined throgh an armarx::StationaryObject. The armarx::StationaryObject holds the objedts global pose (armarx::StationaryObject::objectPose) and class (armarx::StationaryObject::objectClassBase)
Add objects from the WorkingMemory
You can add all objects from the WorkingMemory by calling armarx::SimoxCSpace::addObjectsFromWorkingMemory.
Add objects manually
You can manually create a armarx::StationaryObject and add it to the c-space by calling armarx::SimoxCSpace::addStationaryObject.
Add a table:
This adds the object named "table" to the scene. The object is neither translated nor rotated. The code in the comments can be used to check whether the object could be retrieved.
Now we will add a box to the table.
The added box is translated and rotated.
Add the agent
To perform planning you need an agent. You can set the agent by calling armarx::SimoxCSpace::setAgent and passing the armarx::AgentPlanningInformation. The armarx::AgentPlanningInformation holds several members:
- agentProjectName: The project containing the robots descriptionfile.
- agentRelativeFilePath: The descriptionfiles relative path within its project.
- kinemaicChainNames: Kinematic chains used for planning (these define the c-space).
- additionalNodesToPlan: Additional robot nodes used for planning (if you want to allow an additional joint to move, but have no kinematic chain containing all required nodes)
- blacklistedNodes: Nodes not to move (it overrides any ways to add nodes). This is useful if you only want a subset of a kinematic chain to move.
- collisionSetNames: Sets used for collision checking (Collisions will be checked between sets, too)
- attachedObjects: You can attach objects to the agent (e.g. If the agent is holding something in its hand.). (See section Attach objects)
- initialJointValues: Some nodes may need an intial value during planning (e.g. the left arm should have some pose, while the right arm is planned.). Put these values in this map.
- agentPose: The agent's global pose
An agent's creation could look like this:
Attach objects
If the agent holds an object you may want to check it for collisions, too. To do this you can add an (or several) armarx::AttachedObject to the armarx::AgentPlanningInformation.
You will need to load the object you want to attach and set the value armarx::AttachedObject::objectClassBase.
The given collision set name (armarx::AttachedObject::associatedCollisionSetName) is used to suppress collision checks. This can be used to stop collision checking between the hand holding an object and the object. If left empty all collisions will be checked.
The object is attached to the robot node given in armarx::AttachedObject::attachedToRobotNodeName.
Now you need to set the relative position between the robot node and the object. This may be a grasp you just planned or used.
Finally add the attached object to the agent and set the cspaces agent.
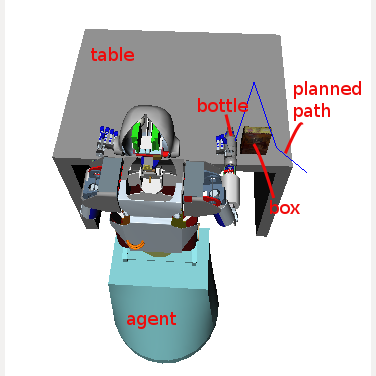
The created scene looks like this: